Types Of Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a disorder of the brain. People are diagnosed with epilepsy when they have had two or more seizures.
There are many types of seizures. A person with epilepsy can have more than one type of seizure. The signs of a seizure depend on the type of seizure.
By classifying the type of seizure, a patient may get help about the healthcare and can choose the right therapy for the patient.
Types of epilepsy and their symptoms
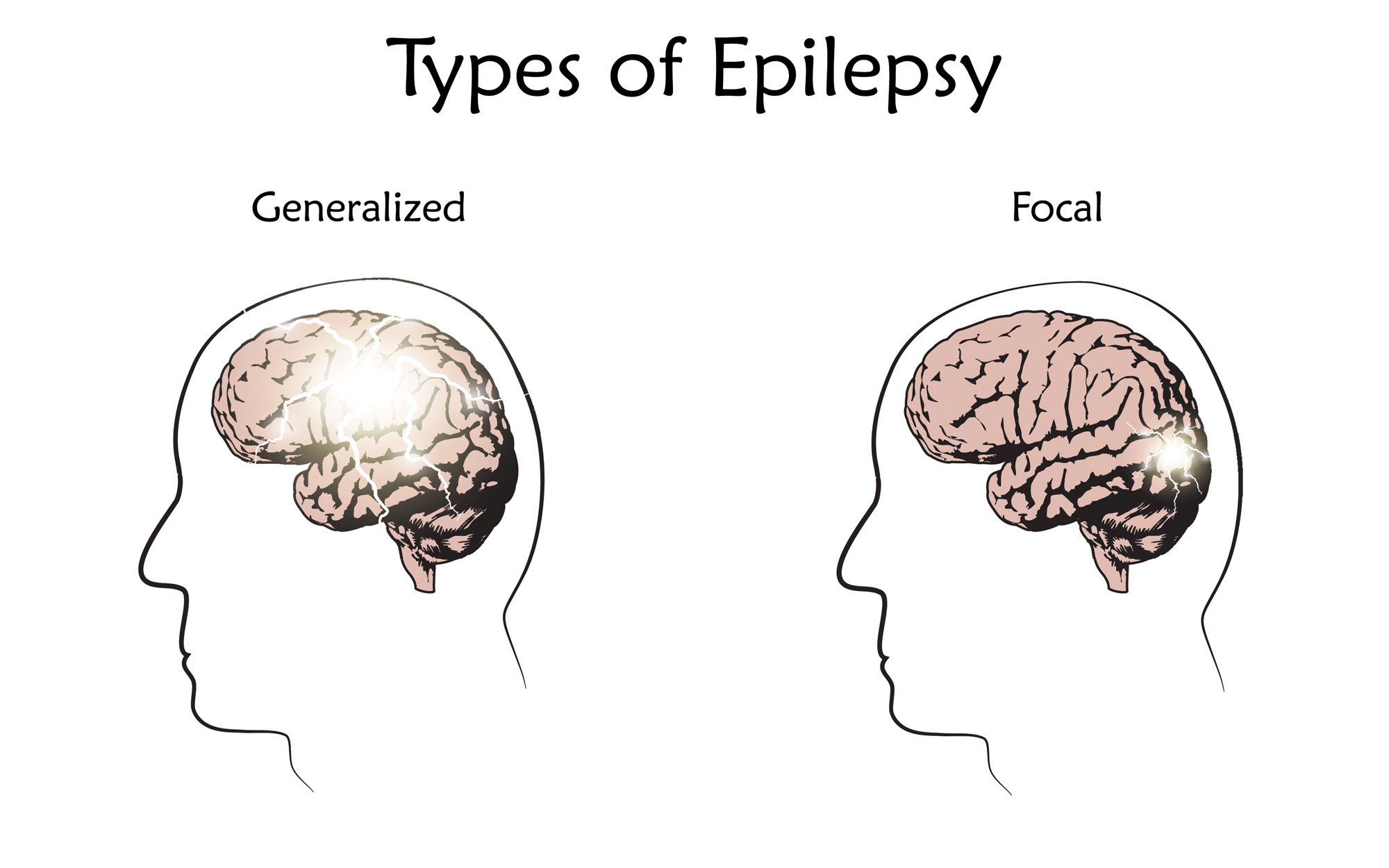
There are two basic types of epilepsy:
- Generalized epilepsy
- Focal (partial) epilepsy
The difference between these two types of epilepsy is how and where they begin in the brain.
Generalized seizures affect both sides of the brain and cause loss of consciousness. Approximately 23% to 35% of epilepsy are generalized.
It includes the following seizures:
• Absence seizures (Petit Mal seizures) can cause rapid blinking, a few seconds of staring into space, lack of awareness, confusion, or slight muscle twitching.
• Tonic-clonic seizures (Grand Mal seizures) can make a person cry out, lose consciousness, fall to the ground, or have muscle jerks or spasms. The person may feel tired after a tonic-clonic seizure.
• Myoclonic seizures are brief, lasting a few seconds or less. Symptoms include staying fully or partially conscious, increase in muscle tone of some muscles, or possible altered sensations, such as a sensation of an electric shock
Focal seizures are located in just one area of the brain. These seizures are also called partial seizures. About 60% of all types of epilepsy are focal.
Seizures in this category include:
• Simple focal seizures affect a small part of the brain. These seizures can cause twitching or a change in sensation, such as a strange taste or smell or feeling of déjà vu.
• Complex focal seizures can make a person with epilepsy confused or stunned. The person will be unable to respond to questions or directions for up to a few minutes.
Combined generalized and focal epilepsy-
This type of seizure begins in one part of the brain, but then spreads to both sides of the brain. In other words, the person first has a focal seizure, followed by a generalized seizure. Seizures may last as long as a few minutes.
The seizures can occur together or separately. One type of seizure can occur more frequently than others. The exact symptoms depend on the seizures involved.