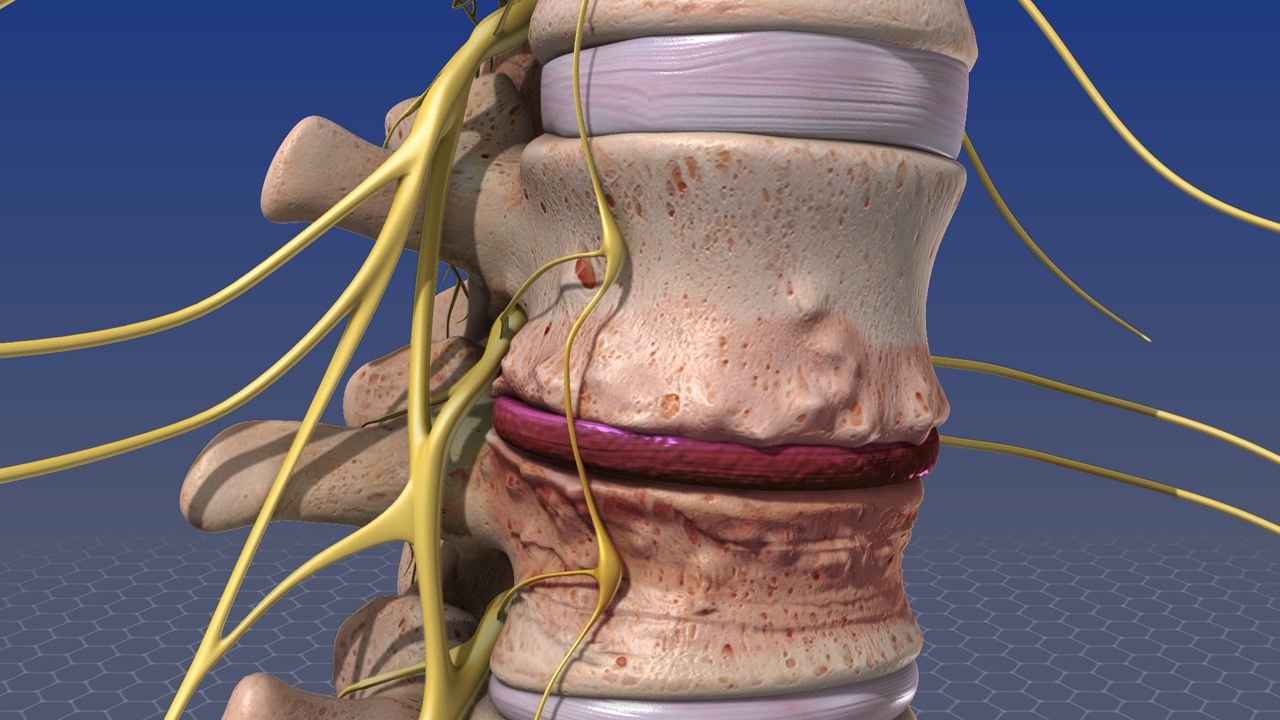
Infections of Spinal Cord
Spinal infection is a rare, but often serious, form of the disease that occurs when bacteria, fungi, or viruses invade the spinal tissues. These foreign agents can attack the vertebrae, spinal discs, meninges, spinal canal, and even the spinal cord. While rare, infections of the spine are possible and can occur in the intervertebral disc of the spine (referred to as “discitis”) or the vertebral bones of the spine (referred to as “osteomyelitis”) Typically, these infections spread to the spine through the bloodstream. When a spinal infection occurs, the bone can begin to deteriorate and collapse upon itself.
Types
The types of spinal infections include Vertebral Osteomyelitis (These infections most often occur in the lumbar spine and can cause pain in the arm or leg, fever, and problems with walking or using your hands), Discitis (This uncommon infection can occur on its own or after surgery Meningitis (Causing swelling in the tissues around the brain and spine) and Spinal cord abscess (This infection is caused internally in the spine and is very rare. It can cause fever, back pain and a decline in spine function).
Causes
Spinal infections can be caused by either a bacterial or a fungal infection in another part of the body that has been carried into the spine through the bloodstream which weakens the immune system and can lead to a spinal infection. In addition, if the person has recently undergone spine or pelvic surgery, then the risk of contracting a spinal infection rises abruptly. Infections, like pneumonia and tuberculosis, can also spread to the spine from the lungs. Other events that increase the risk include vein drug use, long-term use of steroids, and spinal trauma.
Symptoms
The symptoms may vary depending on the type of spinal infection but, generally, pain is localized initially at the site of the infection. The diseases caused by spine infections include these symptoms like severe back pain, fever, chills, weight loss, muscle spasms, painful or difficult urination, weakness of voluntary muscles and bowel/bladder dysfunction, and paralysis.
Treatment
The biggest challenge is making an early diagnosis before serious illness occurs. Spinal infections often require long-term antibiotics or antifungal therapy. Restriction in movement may be recommended when there is significant pain or the potential for spine instability. The type of medication is determined on a basis depending on the patient’s specific circumstances, including his or her age.
Treatment At Home
Proper and timely follow-up is necessary to ensure that the spinal infection has been controlled and is responding to the treatment protocol. To treat spinal infection, a doctor will prescribe antibiotics and bracing to support the spine as it heals. For that proper rest is required and the medicines will be sufficient to help it recover.
When to seek a neurologist?
Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent the progression of the infection. Delaying care may result in the progression of the infection causing damage to soft tissue structures of and around the spine. A person should seek medical care if symptoms of a spinal infection are present.